TASK ANALYSIS
WHAT IS TASK ANALYSIS?
A task analysis is a fundamental tool for teaching life skills. It
is how a specific life skill task will be introduced and taught. The choice of forward or backward chaining will
depend on how the task analysis is written.
A good task analysis consists of a written list of the
discrete steps required to complete a task, such as brushing teeth, mopping a
floor, or setting a table. The task analysis is not meant to be given to the
child but is used by the teacher and staff supporting the
student in learning the task in question.
TO BE CONSIDERED IN A TA
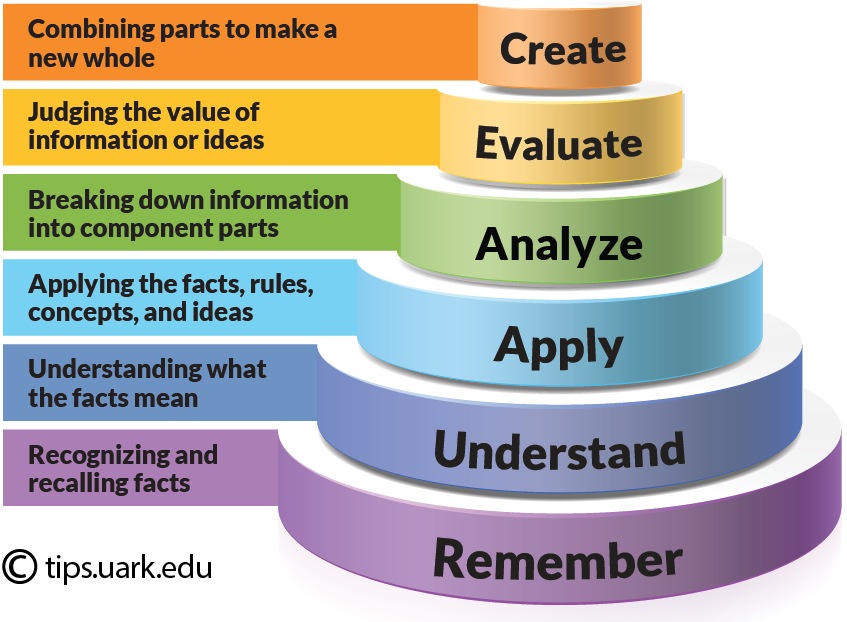
Three levels of knowledges:
ü FACTUAL
ü CONCEPTUAL
ü PROCEDURAL
ü METACOGNITIVE
Task analysis is one of the most effective ways to teach elementary,
secondary, and even college students to thoroughly complete an assignment and
master a skill(s). This article highlights everyday activities that can be
broken into component parts to reach a specific learning goal.
Task analysis, in simple terms, is a process that breaks down an
activity into smaller parts. By using task
analysis in the
classroom, teachers find that goals are more easily reached and that students
are more likely to recall material at a later date. Sequences or steps are
followed and practiced, making complex goals more attainable and hazy
directions clearer!